二、CUDA文档学习-编程模型
从基于NVIDIA Ampere GPU架构的设备开始,CUDA编程模型通过异步。
https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-programming-guide/#
2. Programming Model
2.1. Kernels
由N个不同的CUDA线程并行执行N次,而不是像常规c++函数那样只执行一次。
内核kernel 是使用__global__声明说明符定义的,对于给定的内核调用,执行该内核的CUDA线程数是使用新的<<<…>>>执行配置语法。每个执行内核的线程都有一个唯一的thread ID ,可以通过内置变量在内核中访问。
内置变量threadadIdx
// Kernel definition
__global__ void VecAdd(float* A, float* B, float* C)
{
int i = threadIdx.x;
C[i] = A[i] + B[i];
}
int main()
{
...
// Kernel invocation with N threads
VecAdd<<<1, N>>>(A, B, C);
...
}执行VecAdd()的N个线程中的每一个执行一次成对加法。
2.2. Thread Hierarchy
threadIdx is a 3-component vector, a one-dimensional, two-dimensional, or three-dimensional thread index.形成one-dimensional, two-dimensional, or three-dimensional block of threads,称为线程块 thread block。 vector, matrix, or volume.
index of a thread and its thread ID的关系
- one-dimensional block:same
- two-dimensional block of size (Dx, Dy): thread ID of a thread of index (x, y) is (x + y Dx);
- three-dimensional block of size (Dx, Dy, Dz): thread ID of a thread of index (x, y, z) is (x + y Dx + z Dx Dy)
// Kernel definition
__global__ void MatAdd(float A[N][N], float B[N][N],
float C[N][N])
{
int i = threadIdx.x;
int j = threadIdx.y;
C[i][j] = A[i][j] + B[i][j];
}
int main()
{
...
// Kernel invocation with one block of N * N * 1 threads
int numBlocks = 1;
dim3 threadsPerBlock(N, N);
MatAdd<<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>(A, B, C);
...
}每个块的线程数是有限制的 the number of threads per block,因为一个块的所有线程 all threads of a block 都被期望驻留在同一个流多处理器核心上 the same streaming multiprocessor core,并且必须共享该核心有限的内存资源share the limited memory resources of that core。在当前的gpu上,一个线程块可能包含多达1024个线程。
一个内核kernel 可以由多个形状相等的线程块执行multiple equally-shaped thread blocks,因此线程总数total number of threads等于每个块的线程数 number of threads per block乘以块的数量number of blocks。
块Blocks 被组织成一维、二维或三维线程块网格one-dimensional, two-dimensional, or three-dimensional grid of thread blocks ,网格中的线程块的数量number of thread blocks通常由正在处理的数据的大小决定,这通常超过系统中的处理器数量number of processors in the system。
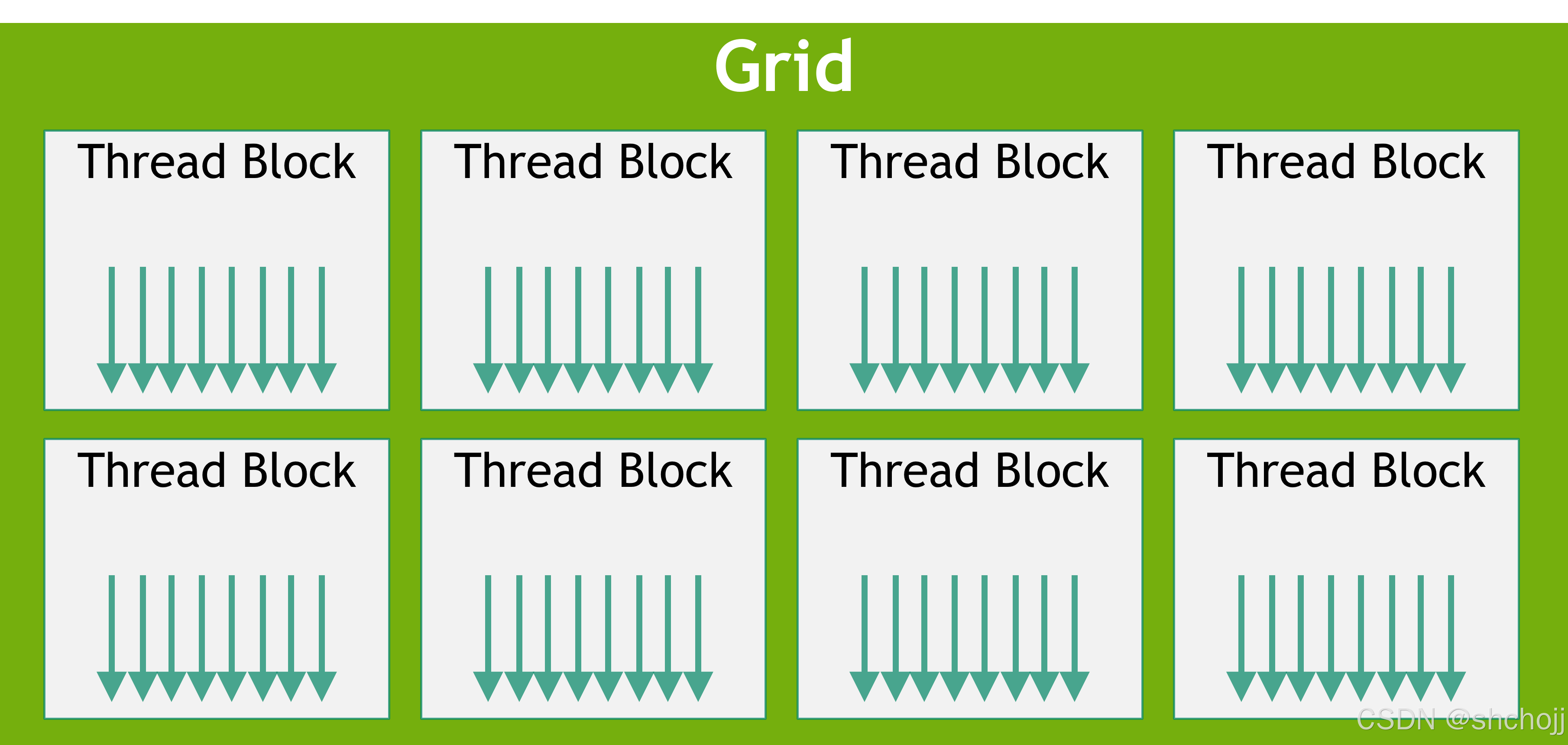
Figure 4 Grid of Thread Blocks
每个块的线程数number of threads per block和每个网格的块数the number of blocks per grid在<<<…>>>语法可以是int或dim3类型。可以按照上面的示例指定二维块Two-dimensional blocks 或网格grids。
网格grid 中的每个块block 都可以通过一个一维、二维或三维one-dimensional, two-dimensional, or three-dimensional 唯一索引来标识,该索引可以通过内置的blockIdx变量在内核中访问。线程块的维度The dimension of the thread block可以通过内置的blockDim变量在内核中访问。
// Kernel definition
__global__ void MatAdd(float A[N][N], float B[N][N],
float C[N][N])
{
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
int j = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
if (i < N && j < N)
C[i][j] = A[i][j] + B[i][j];
}
int main()
{
...
// Kernel invocation
dim3 threadsPerBlock(16, 16);
dim3 numBlocks(N / threadsPerBlock.x, N / threadsPerBlock.y);
MatAdd<<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>(A, B, C);
...
}线程块大小为16x16(256个线程),虽然在这种情况下是任意的,但这是一种常见的选择。网格grid 是用足够的块blocks 创建的,每个矩阵元素 per matrix element 像以前一样有一个线程 one thread。为简单起见,本例假设每个维度中每个网格的线程数the number of threads per grid可以被该维度 each dimension中每个块的线程数整除 the number of threads per block,尽管事实并非如此。
线程块Thread blocks需要独立执行 execute independently:必须能够以任意顺序、并行或串联执行它们。这种独立性要求允许在任意数量的内核any number of cores 上以任意顺序调度线程块 thread blocks。
块内的线程Threads within a block 可以通过共享内存shared memory共享数据sharing data,并通过同步synchronizing 执行来协调内存访问coordinate memory accesses。更准确地说,可以通过调用__syncthreads()内部函数来指定内核中的同步点 synchronization points in the kernel ;__syncthreads()作为一个屏障barrier ,块中的所有线程threads in the block必须在允许任何线程继续之前等待wait 。共享内存 Shared Memory 给出了一个使用共享内存的例子。除了__syncthreads()之外,协作组API Cooperative Groups API 还提供了一组丰富的线程同步原语thread-synchronization primitives。
为了高效的协作,共享内存shared memory应该是靠近每个处理器核心的低延迟内存 low-latency memory (很像L1缓存),__syncthreads()应该是轻量级lightweight的。
2.2.1. Thread Block Clusters
随着NVIDIA Compute Capability 9.0的推出,CUDA编程模型引入了一个可选的层次结构级别level of hierarchy,称为线程块集群(Thread Block Clusters),由线程块组成thread blocks。类似于线程块中的线程threads in a thread block保证在流多处理器streaming multiprocessor上被共同调度,集群中的线程块thread blocks in a cluster 也保证在GPU中的GPU处理集群(GPU Processing Cluster, GPC)上被共同调度。
与线程块thread blocks类似,集群clusters 也被组织成一维、二维或三维one-dimension, two-dimension, or three-dimension ,如线程块集群网格Grid of Thread Block Clusters所示。集群中的线程块数量The number of thread blocks in a cluster可以自定义,并且在CUDA中最多支持8个线程块a maximum of 8 thread blocks in a cluster 作为可移植集群大小a portable cluster size in CUDA。请注意,在GPU硬件或MIG配置太小而无法支持8个多处理器的情况下,最大集群大小将相应减少。识别这些较小的配置,以及支持线程块集群大小超过8的较大配置,是特定于体系结构的,可以使用cudaOccupancyMaxPotentialClusterSize API进行查询。
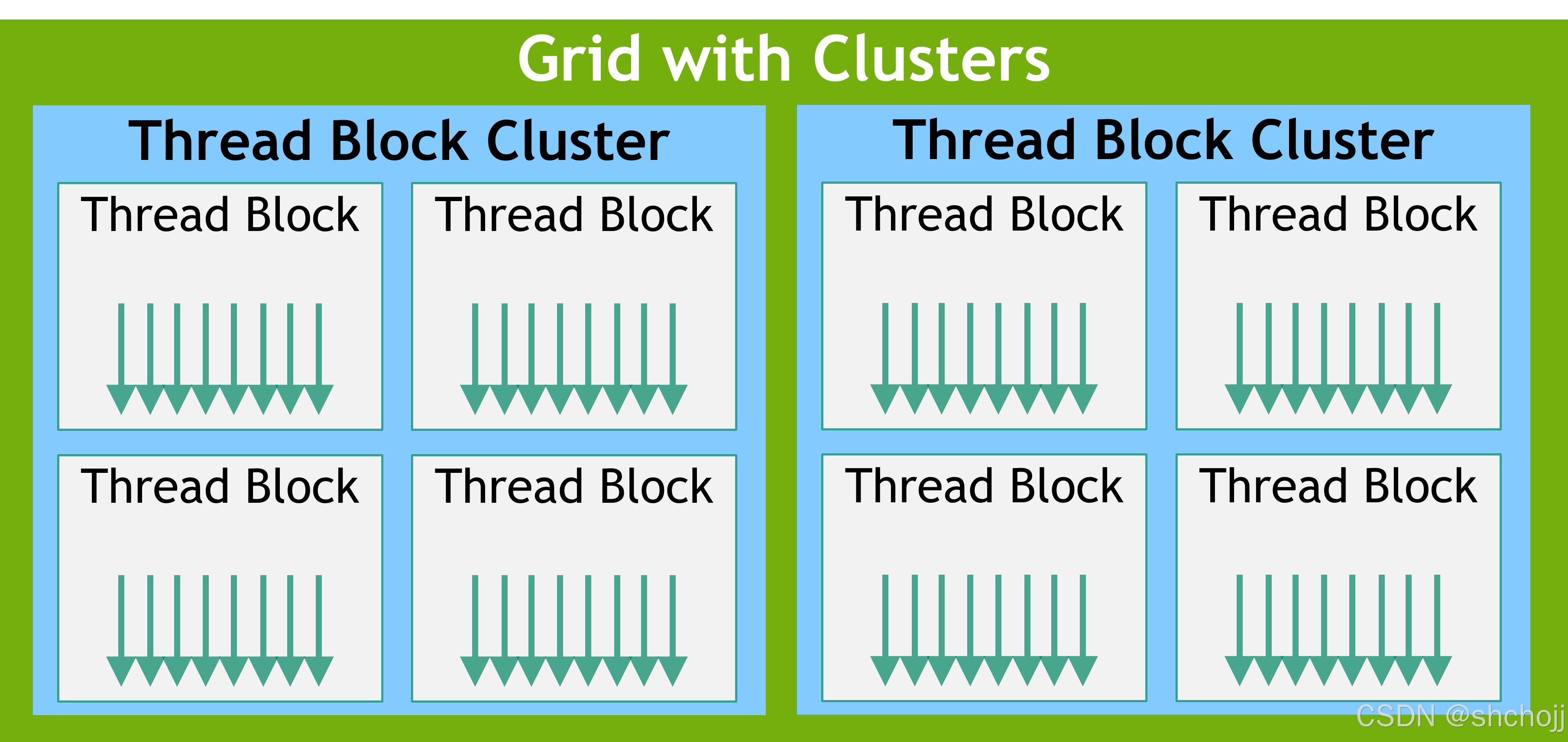
Figure 5 Grid of Thread Block Clusters
在使用集群支持启动的内核中,出于兼容性的考虑,gridDim变量仍然以线程块的数量表示大小 number of thread blocks。可以使用Cluster Group API找到集群中块的秩The rank of a block in a cluster 。
线程块集群A thread block cluster 可以在内核kernel 中使用编译器时间内核compiler time kernel attribute 属性__cluster_dims__(X,Y,Z)或使用CUDA内核启动API cudaLaunchKernelEx来启用。下面的示例展示了如何使用编译器时间内核属性compiler time kernel attribute启动集群。使用内核属性的集群大小在编译时是固定的,然后可以使用经典的<<<,>>>启动内核。如果内核使用编译时集群大小,则在启动内核时不能修改集群大小。
// Kernel definition
// Compile time cluster size 2 in X-dimension and 1 in Y and Z dimension
__global__ void __cluster_dims__(2, 1, 1) cluster_kernel(float *input, float* output)
{
}
int main()
{
float *input, *output;
// Kernel invocation with compile time cluster size
dim3 threadsPerBlock(16, 16);
dim3 numBlocks(N / threadsPerBlock.x, N / threadsPerBlock.y);
// The grid dimension is not affected by cluster launch, and is still enumerated
// using number of blocks.
// The grid dimension must be a multiple of cluster size.
cluster_kernel<<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>(input, output);
}线程块集群大小A thread block cluster size也可以在运行时runtime 设置,内核可以使用CUDA内核启动API cudaLaunchKernelEx启动。下面的代码示例展示了如何使用可扩展API启动集群内核。
// Kernel definition
// No compile time attribute attached to the kernel
__global__ void cluster_kernel(float *input, float* output)
{
}
int main()
{
float *input, *output;
dim3 threadsPerBlock(16, 16);
dim3 numBlocks(N / threadsPerBlock.x, N / threadsPerBlock.y);
// Kernel invocation with runtime cluster size
{
cudaLaunchConfig_t config = {0};
// The grid dimension is not affected by cluster launch, and is still enumerated
// using number of blocks.
// The grid dimension should be a multiple of cluster size.
config.gridDim = numBlocks;
config.blockDim = threadsPerBlock;
cudaLaunchAttribute attribute[1];
attribute[0].id = cudaLaunchAttributeClusterDimension;
attribute[0].val.clusterDim.x = 2; // Cluster size in X-dimension
attribute[0].val.clusterDim.y = 1;
attribute[0].val.clusterDim.z = 1;
config.attrs = attribute;
config.numAttrs = 1;
cudaLaunchKernelEx(&config, cluster_kernel, input, output);
}
}在具有计算能力9.0的GPU中,集群中的所有线程块all the thread blocks in the cluster都保证在单个GPU处理集群(a single GPU Processing Cluster, GPC)上共同调度 co-scheduled,并允许集群中的线程块 thread blocks in the cluster 使用Cluster Group API cluster.sync()执行硬件支持的同步hardware-supported synchronization。集群组Cluster group还提供了成员函数,分别使用num_threads()和num_blocks() API以线程数 number of threads 或块数 number of blocks来查询集群组大小cluster group size。可以通过dim_threads()和dim_blocks() API分别查询集群组 cluster group 中线程和块thread or block的排名。
属于集群cluster 的线程块Thread blocks可以访问分布式共享内存Distributed Shared Memory。集群中的线程块Thread blocks in a cluster能够对分布式共享内存中的任何地址进行读、写和执行原子atomics 操作。分布式共享内存distributed shared memory给出了一个在分布式共享内存Distributed Shared Memory 中执行直方图的示例。
2.3. Memory Hierarchy
CUDA线程threads 可以在执行期间访问多个内存空间 multiple memory spaces中的数据,如图6所示。每个线程都有私有的本地内存private local memory。每个线程块thread block 都有共享内存 shared memory ,对该块的所有线程all threads of the block 可见,并且与该块block具有相同的生存期lifetime 。线程块集群 a thread block cluster中的线程块Thread blocks 可以在彼此的共享内存上shared memory执行读、写和原子atomics 操作。所有线程threads 都可以访问相同的全局内存the same global memory。
还有两个额外的只读内存空间 read-only memory spaces可供所有线程访问:常量和纹理内存空间the constant and texture memory spaces。全局、常量和纹理内存空间The global, constant, and texture memory spaces针对不同的内存使用进行了优化(参见 Device Memory Accesses)。纹理内存Texture memory还提供了不同的寻址模式addressing modes,以及一些特定数据格式 data formats的数据过滤 data filtering(参见Texture and Surface Memory)。
全局、常量和纹理内存空间The global, constant, and texture memory spaces 在同一个应用程序的内核启动期间是持久的。
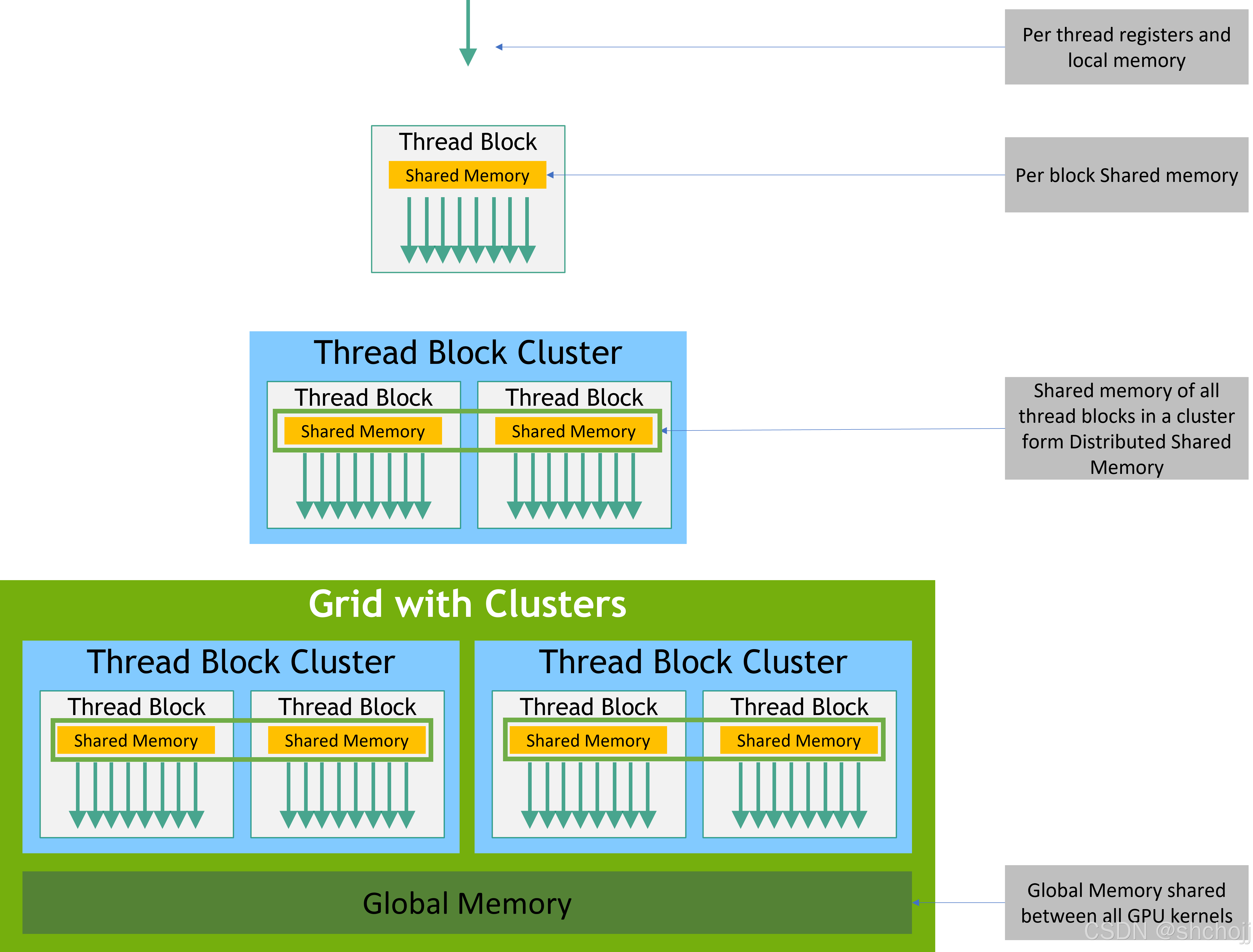
Figure 6 Memory Hierarchy
2.4. Heterogeneous Programming
如图7所示,CUDA编程模型假设CUDA线程threads 在物理上独立的设备上执行,该设备作为运行c++程序的主机host 的协处理器运行。例如,当内核在GPU上执行而c++程序的其余部分在CPU上执行时,就是这种情况。
CUDA编程模型还假设主机host 和设备device 在DRAM中保持各自独立的内存空间 separate memory spaces ,分别称为主机内存和设备内存host memory and device memory。因此,程序通过调用CUDA运行 CUDA runtime时(在编程接口中描述)来管理内核kernels可见的全局、常量和纹理内存空间 global, constant, and texture memory spaces 。这包括设备内存分配allocation 和回收deallocation ,以及主机和设备内存host and device memory之间的数据传输。
统一内存Unified Memory提供托管内存managed memory来连接主机和设备内存空间the host and device memory spaces。系统中的所有cpu和gpu都可以访问托管内存Managed memory,作为具有公共地址空间 a common address space的单个连贯内存映像a single, coherent memory image 。此功能支持设备内存的超额订阅oversubscription of device memory ,并且可以通过消除在主机和设备上 host and device显式镜像数据explicitly mirror data的需要,大大简化移植应用程序的任务。有关Unified Memory Programming的介绍,请参阅统一内存编程。
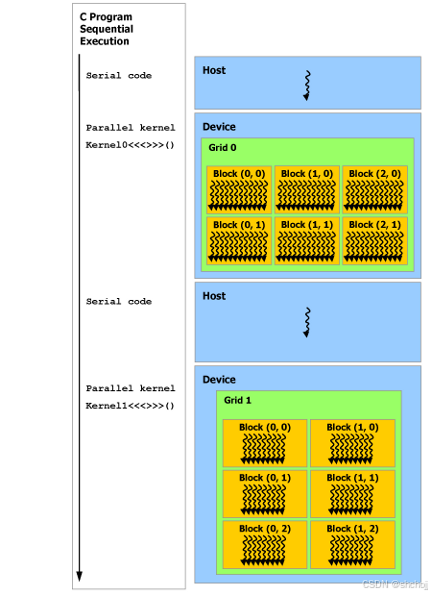
Figure 7 Heterogeneous Programming
串行代码Serial code在主机host上执行,并行代码parallel code 在设备device上执行。
2.5. Asynchronous SIMT Programming Model
在CUDA编程模型中,线程是执行计算或内存操作的最低抽象级别a thread is the lowest level of abstraction。从基于NVIDIA Ampere GPU架构的设备开始,CUDA编程模型通过异步asynchronous 编程模型为内存操作提供加速。异步asynchronous 编程模型定义了与CUDA线程相关的异步操作的行为。
异步asynchronous编程模型为CUDA线程之间的同步synchronization 定义了Asynchronous Barrier的行为。该模型还解释并定义了cuda::memcpy_async如何用于在GPU计算时从全局内存global memory 异步移动数据move data asynchronously。
2.5.1. Asynchronous Operations
异步操作 asynchronous operation被定义为由CUDA线程发起并由另一个线程异步执行asynchronously的操作。在一个格式良好的程序中,一个或多个CUDA线程与异步操作同步 CUDA threads synchronize with the asynchronous operation。发起异步操作asynchronous operation的CUDA线程不需要在同步线程synchronizing threads中。
这样的异步线程asynchronous thread(as-if线程)总是与发起异步操作asynchronous operation的CUDA线程相关联。异步操作 asynchronous operation 使用同步对象 synchronization object来同步synchronize 操作的完成。这样的同步对象可以由用户显式地管理(例如,cuda::memcpy_async)或隐式地在库中管理(例如,cooperative_groups::memcpy_async)。
同步对象synchronization object可以是cuda::barrier或cuda::pipeline。这些对象在Asynchronous Barrier和 Asynchronous Data Copies using cuda::pipeline有详细的解释。这些同步对象synchronization objects可以在不同的线程作用域 different thread scopes中使用。作用域scope定义了一组可以使用同步对象synchronization object与异步操作asynchronous operation同步synchronize 的线程。下表定义了CUDA c++中可用的线程范围the thread scopes 以及可以与每个线程同步synchronized 的线程。
|
Thread Scope |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
只有发起异步操作 initiated asynchronous operations的CUDA线程进行同步。 |
|
|
与初始线程同步initiating thread synchronizes的同一线程块the same thread block内的所有或任何CUDA线程。 |
|
|
与初始线程同步的同一same GPU设备中的所有或任何CUDA线程。 |
|
|
与初始线程在同一系统system 中的所有或任何CUDA或CPU线程同步。 |
这些线程作用域是在CUDA Standard C++库中作为标准c++的扩展实现的。
2.6. Compute Capability
设备的计算能力由版本号表示,有时也称为“SM版本”。
计算能力由主修订号X和次修订号Y组成,用x.y表示
基于NVIDIA Hopper GPU架构的设备的主要修订号为9,
基于NVIDIA Ampere GPU架构的设备的主要修订号为8,
基于Volta架构的设备的主要修订号为7,
基于Pascal架构的设备的主要修订号为6,
基于Maxwell架构的主要修订号为5,基于Kepler架构的主要修订号为3。
图灵是用于计算能力为7.5的设备的架构,是基于Volta架构的增量更新。
所有CUDA-Enabled设备的CUDA-Enabled GPUs以及它们的计算能力。“ Compute Capabilities”给出了每种计算能力的技术规格。
特定GPU的计算能力版本不应与CUDA版本(例如,CUDA 7.5, CUDA 8, CUDA 9)混淆,CUDA版本是CUDA软件平台的版本。
从CUDA 7.0和CUDA 9.0开始,Tesla和Fermi 架构将不再被支持。

欢迎来到由智源人工智能研究院发起的Triton中文社区,这里是一个汇聚了AI开发者、数据科学家、机器学习爱好者以及业界专家的活力平台。我们致力于成为业内领先的Triton技术交流与应用分享的殿堂,为推动人工智能技术的普及与深化应用贡献力量。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容






所有评论(0)